Generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools equivalent to ChatGPT or Dall E are changing the way in which creative work is completed, particularly in industries that depend on innovation.
However, the usage of AI within the innovation process requires careful consideration. Our research shows that the important thing to success lies in understanding and leveraging the several but complementary roles of humans and AI.
Innovation is important for each company that desires to achieve success today. Actually, 83 percent of corporations see innovation as a top priorityYet only three percent are willing to make this priority a reality. This shows how much corporations need to enhance their approach to innovation.
Innovation is about solving complex problems that result in real improvements. It's not nearly coming up with good ideas; Knowledge workIt is the means of using information to create something of value.
Generative AI may help corporations prepare for innovation by facilitating knowledge work, but its full potential is yet to be present in this area not fully understood.
(Shutterstock)
Design sprints
Our team, consisting of educational researchers with expertise in emerging digital technologies and a practitioner with experience in leading human-centered innovation projects, conducted a detailed study how generative AI was utilized in design sprints in three organizations. (The study is accessible as a preprint and has been submitted to a specialist journal for review.)
A Design Sprint is a fast, structured process for solving key problems that helps teams test whether a product, service or strategy is working. Sprints are useful because they reduce the risks and costs of traditional product development
During a design sprint, a small team of 5 to seven employees from different areas works intensively together for a number of days to resolve an issue. Their work is coordinated by a facilitator who organizes activities, leads the team, tracks progress, ensures that goals are clear and that point is used efficiently.
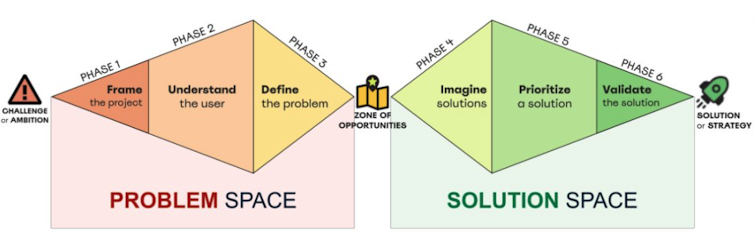
The first phase of a design sprint is about understanding and defining the issue, while the second phase is about constructing and testing an answer. In each phases, teams must adopt two key mindsets:
-
Divergent ponderingwhich suggests developing many various ideas and possibilities.
-
Convergent ponderingwhich suggests narrowing down those ideas to discover priorities or solutions.
Our study examined how the presenter used generative AI tools equivalent to ChatGPT, DALL-E 3 or… Uizard to assist the team engage effectively in each divergence and convergence.
(Cédric Martineau, Carverinno Conseil)
AI and humans work together
When it involves divergent pondering activities, we found two foremost advantages of using generative AI. First, it encouraged teams to explore more possibilities by providing basic ideas as a place to begin. Secondly, it helped to rephrase and summarize team members' unclear ideas, which ultimately led to raised communication throughout the teams.
One participant told us:
“Sometimes we had plenty of ideas and the AI summarized them in a concise text. This allowed us to be clear about it. It gave us a foundation, there have been plenty of fragmented ideas that everybody contributed and now we had a text that all of us agreed on. In this fashion, we began from the identical base, which served as a springboard for further development.”
So the true value of generative AI lay not in coming up with sensible latest ideas itself, but within the invaluable synergies that arose from the method. Team members leveraged their contextual knowledge and remained in charge of the method, while AI helped higher communicate their ideas, expand exploration, and eliminate potential blind spots.

(Shutterstock)
Make higher informed decisions
We noticed different dynamics in convergence activities where teams needed to make decisions after difficult idea generation sessions. By this point, team members were normally mentally exhausted. The generative AI was particularly helpful on this part to do the heavy lifting.
AI helped handle the information-intensive tasks required for team alignment, equivalent to: B. Reformulating, summarizing, organizing, comparing, and rating options. This reduced the mental load on team members and allowed them to deal with vital tasks like evaluating ideas. In this process the team was answerable for:
- AI Output Review to make sure the content is accurate and useful. For example, ChatGPT and Uizard helped create design scenarios and prototype designs to validate their concept, however the team still needed to refine them to attain the project goals.
- Adding your individual insights and contextual nuances to guide final decisions, bearing in mind aspects equivalent to feasibility, ethics and long-term strategic implications.
One participant said:
“Sometimes the AI focused on details that were insignificant to us… Sometimes we would have liked less general synthesis and more personalized input.”
Overall, this manner of human-AI collaboration on convergent activities helped the team make more informed and assured decisions about which problem to deal with and which solution to pursue. This gave them a way of control over the ultimate results of the sprint.
One participant said:
“If we relied solely on AI to find out what was vital at crucial stages like decision making or voting on something vital like successful factor, there could be pushback.” We are in a greater position to know . We are the individuals who will implement the ultimate solution.”
Challenges and opportunities
In line with research too cognitive automation And Intelligent automationWe've found that generative AI is an enormous assist in tackling cognitively demanding tasks like reformulating poorly formulated ideas, summarizing information, and identifying patterns in team members' contributions.
A key challenge in using generative AI in innovation is ensuring that it complements, reasonably than replaces, human engagement. While AI can function a useful companion, there’s a risk that if used excessively, it could possibly impact team engagement or ownership of the project.
The Design Sprint presenter told us:
“Feasibility have to be balanced with desirability. Technically you possibly can automate a lot of the process, but that may destroy the necessity for pleasure and interaction and other people's doubts aren’t taken under consideration; Additionally, people have to own the issue – all of those are essential elements in a human-centered innovation process.”
Therefore, often assessing the impact of AI on this process is crucial to take care of a healthy balance. Automation should encourage creativity and decision-making without undermining the human insights which can be central to innovation.
As AI continues to develop, its role in innovation will increase. Companies that integrate AI into their workflows are higher equipped to fulfill the fast-moving demands of recent innovation. However, it is necessary to know each the strengths and limitations of AI and humans to make sure this collaboration is effective.

