In sport, the border between success and failure is commonly measured in Milliseconds. It might be a cricket player who might be his foot position, a runner who refines his sprint start, or a footballer who perfects her death.
This is where movement recording comes into play – to the numerous approaches used for sporting performance and movement evaluation.
Conventional motion recording follows the movements of an individual by utilizing sensors or reflective markers related to cameras. This provides data with which sports scientists analyze how an athlete's performance improves, personalized your training program and stop possible injuries.
But for a long time, the motion capture has been carried out in sports with cumbersome suits and sophisticated camera systems. These technologies offer high precision, but have remained out of reach for a lot of as a consequence of their costs, technical requirements and rigid laboratory restrictions.
While sport is developing, the technology that it analyzes must also. The way we measure human movement experiences an excellent transformation. Markerless motion recording (Activated by artificial intelligence, computer vision, deep sensors and multiple cameras systems) should revolutionize the sports performance evaluation.
As a Health and sports scientists With a concentrate on data, innovation and technology, I made CO auto -authorized a study on a markerless motion capture in sports and movement. We have checked and compared various options for movement recording in order that users can select which system is best suited to your needs and budgets.
This is essential because markerless motion recording offers a practical alternative that’s accessible, scalable and customizable to real settings. It is a shift that guarantees how athletes train, how they move, how injuries are rated and the way coaches refine the performance.
The problem with traditional motion recording
Marker -based movement recording has long been considered a gold standard for the evaluation of the movement. Various systems use optoelectronic (devices that output or recognize light) persecution. You have provided researchers and trainers precisely three -dimensional (3D) data on joint angles, movement efficiency and biomechanical stress. But these systems are related to challenges.
With the sort permission of Habib Noorbhai
First, the necessity for reflective markers, that are placed on the body, leads variability. Even slight incorrect deposits can affect the accuracy of the information.
Second, these systems are largely limited to laboratory environments. Although you’re well fitted to controlled studies, you can not at all times record the dynamics of real sports performance.
Third, the prices for such setups that always reach tens of hundreds of dollars limit their use to elite teams and well-financed research laboratories. This financial barrier places the technology for basic sport outside the range, where the talent development is of crucial importance.
The rise of the markerless movement recording
The marker -free motion capture, driven by Deep Learning and Computer Vision, enables direct movement directly from video film material without requiring physical markings. Models reminiscent of OpenPark, Tensorflow Pose estimate and metrabs can now discover and analyze human joint positions in 3D, all from a single video feed.
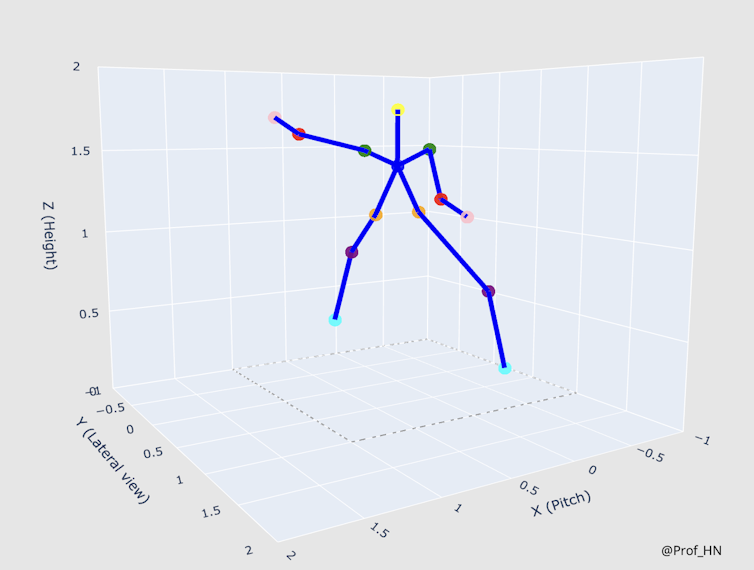
With the sort permission of Habib Noorbhai
This approach has profound effects. This implies that trainers can capture real -time movement data from training units without interrupting the natural game flow. Athletes can analyze their technology with nothing greater than a smartphone camera. It opens the door for the motion capture to go over the laboratory and on the sphere, the farm or the gym.
Where markerless motion recording works best
The ability to pursue the movement in real environments makes markerless motion recording in high-speed and dynamic sport.
In football, the persecution of the player movement can influence tactical decisions in the course of the transition from exercises. During the sprint, trainers can analyze the strid length and the bottom contact time without disturbing the training sessions. In baseball and cricket, the impact mechanics will be assessed without having to wear minor tracking suits or markings.
In addition to the performance evaluation, the consequences on injury management and rehabilitation are only as convincing.
By integrating the markerless movement recording in injury rehabilitation programs, physiotherapists can monitor movement defects in real time. A player who’s recovered by you front cruciate ligament For example, injury can have theirs Gait And Knee -up Angle Remote monitored. This reduces the necessity for repeated clinic visits.
Barriers
Despite its potential, the markerless movement recording just isn’t without challenges. While Deep Learning models improve, you continue to have problems with occlusion: where body parts are temporarily not visible. Variations of lighting, camera hinges and the body varieties of the players can even affect tracking accuracy.
In order to enhance robustness in various sports, these problems should be repeatedly refined in Posen estimation algorithms. (These are computer vision techniques which might be used to locate and persecute the keys on the body on one person in a video.)
Another vital restriction is validation. Conventional motion enclosure systems have been tested extensively for accuracy, but markerless models are still validated in sports -specific contexts.
The guarantee of consistency and reliability can be of crucial importance so as to persuade elite teams to maneuver away from marker-based setups.
A future and not using a marker?
The query stays: Will the marker movement completely disturb and replace traditional systems? The reality will probably be more nuanced.
While the marker-based motion capture maintains its place in highly controlled research settings, markerless alternatives dominate practical, field-based applications. The accessibility, user -friendliness and real -time capabilities of markerless systems make you a player.
If AI models develop into more demanding and sensor technology progresses, the precision of markerless systems will further improve. The way forward for motion recording just isn’t to exchange one method with one other, but several approaches to create a seamless, scalable and precise framework for the movement evaluation.
The query isn’t any longer relating to the query of whether markerless motion recording, but when. And when the technology matures, the benefits for trainers, athletes and scientists will proceed to grow alike. It will play a crucial role within the design of the following generation of sporting performance and movement evaluation.

