People often take walking with no consideration. We just take it one step at a time without ever serious about what it can take to realize this. But each step is a unprecedented act of coordination, controlled by precise timing between the spinal cord, brain, nerves, muscles and joints.
In the past, people have used stopwatches, cameras, or trained eyes to evaluate walking and its deficits. Recent technological advances reminiscent of Motion captureWearable sensors and data science methods will be used to capture and quantify features of step-by-step movements.
We are researchers who study biomechanics and human performance. We and other researchers are increasingly using this data to enhance human movement. These insights not only help athletes of all stripes exceed their performance limits, but additionally support patient movement recovery through personalized feedback. Ultimately, movement could develop into one other vital sign.
From movement data to performance insights
Researchers around the globe mix physiology, biomechanics and data science to decipher human movements. This interdisciplinary approach sets the stage for a brand new era through which machine learning algorithms find patterns in human movement data collected through continuous monitoring, providing insights that improve health.
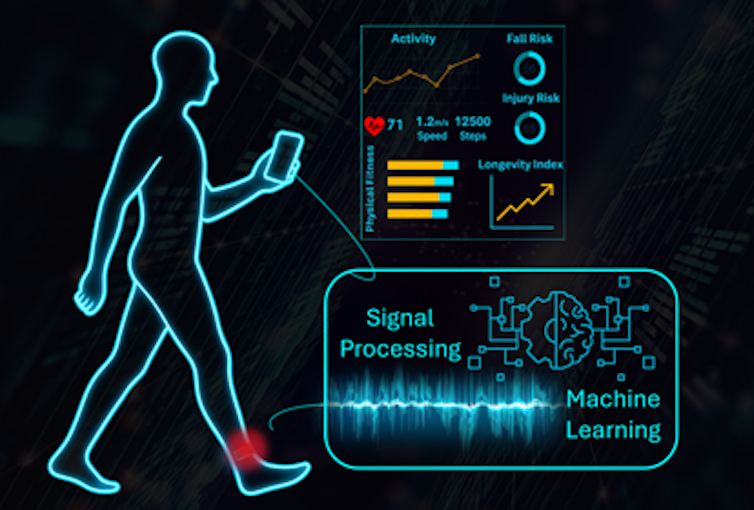
It's the identical technology that powers your fitness tracker. For example this Inertial measurement unit within the Apple Watch records movements and derives measured values reminiscent of variety of steps, stride length and cadence. Wearable sensors, reminiscent of Some devices, reminiscent of inertial measurement devices, record 1000’s of information points every second. The raw data reveals little or no a couple of person's movement. In fact, the info is so noisy and unstructured that it’s unimaginable to achieve meaningful insights.
Institute for Human Performance and Nutrition Research
That's where Signal processing comes into play. A signal is just a sequence of measurements tracked over a time frame. Imagine attaching an inertial measurement unit to your ankle. The device constantly tracks the movement of the ankle by measuring signals reminiscent of acceleration and rotation. These signals provide an outline of the movement and indicate how the body is behaving. However, they often contain unwanted background noise that may blur the actual image.
Using mathematical tools, researchers can filter out the noise and isolate the knowledge that truly reflects the body's performance. It's like taking a blurry photo and using editing tools to make the image clearer. The means of cleansing and manipulating the signals is named signal processing.
After processing the signals, researchers use machine learning techniques to convert them into interpretable metrics. Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence that relies on finding patterns and relationships in data. In the context of human movement, these tools can discover movement characteristics that correspond to necessary performance and health metrics.
For example, our team on the Human Performance and Nutrition Research Institute at Oklahoma State University made an estimate Fitness capability without the necessity for extensive physical testing or special equipment. Fitness capability indicates how efficiently the body can perform physical activity. By combining biomechanics, signal processing and machine learning, we were in a position to estimate fitness capability using data from just just a few steps taken by our subjects.
Beyond fitness, walking data offers even deeper insights. Walking speed is a powerful indicator of longevityand thru tracking we could find out about people's long-term health and life expectancy.
Institute for Human Performance and Nutrition Research
From performance to medicine
The impact of those algorithms goes far beyond tracking performance like steps and miles traveled. They will be used to support rehabilitation and injury prevention. Our team is developing a machine learning algorithm to detect whether an athlete is at increased risk of injury just by analyzing their body movements and detecting subtle changes.
Other scientists have used similar approaches Monitor impairments in motor control After a stroke, how a patient's walking patterns develop is continually assessed to find out whether motor control is improving or whether the patient is compensating indirectly that may lead to a future injury.
Similar tools will also be used to create treatment plans based on the precise needs of every patient, bringing us closer to true personalized medicine. These methods have been utilized in Parkinson's disease diagnose the condition, Monitor severity and recognize episodes of walking difficulty to supply appropriate guidance Notes to patients go on foot again.
Others have used these techniques Designing and controlling wearable aids reminiscent of exoskeletons, which improve the mobility of individuals with physical disabilities by generating electricity at precise intervals. Additionally, researchers have studied exercise strategies in military personnel and located that they’ve poor biomechanics had a better risk of injury. Others have used wrist-worn wearables for detection Overuse injuries in military personnel. At their core, these innovations all have one goal: restoring and improving human mobility.
Movement as an indication of life
We consider the long run of personalized medicine lies in dynamic monitoring. Every step, jump or squat accommodates details about how the body functions, performs and recovers. With advances in wearable technology, AI and cloud computing, real-time motion monitoring and biofeedback are prone to develop into a routine a part of on a regular basis life.
Imagine an athlete's shoe that warns them before an injury occurs, clothing for the elderly that detects and prevents a fall before it occurs, or a smartwatch that uses running behavior to detect early signs of a stroke. By combining biomechanics, signal processing and data science, movement becomes an important sign, a real-time reflection of your health and well-being.

